「親(ちか)しい人に見送られてよかったね」と祖母の亡骸に声をかける。死という、明確な人生のエンドポイント。お世話になった病院の主治医は、48時間前には必ず連絡をしますと約束をしてくれ、家族はとても安心した。
祖母の家をあとに、勉強時間も少し持つことに決め、帰宅後にコクランの”Glossary of Terms in The Cochrane Collaboration”を確認する。
Endpoint ( see outcome)
A component of a participant’s clinical and functional status after an intervention has been applied, that is used to assess the effectiveness of an intervention.
NEJMなどのジャーナルに掲載された心血管関連のランダム化比較試験のエンドポイントの重要性と治療介入効果の関連。
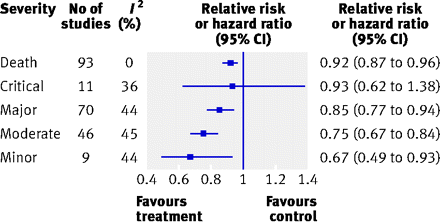
重篤なエンドポイント(死亡,心筋梗塞など,図でのDeath,Critical, Major)は発症数も少なく,治療介入効果も低い。
重要度の低いエンドポイント(狭心症の悪化など,図ではModerateおよびMinor)ほど発症は多く,治療効果も高いと報告されている。対照群の発症率はDeath 3.3%,Critical 3.3%,Major 3.7%,Moderate 12.3%,Minor 8.0%。
Problems with use of composite end points in cardiovascular trials: systematic review of randomised controlled trials
BMJ 2007;334:786

Objective To explore the extent to which components of composite end points in randomised controlled trials vary in importance to patients, the frequency of events in the more and less important components, and the extent of variability in the relative risk reductions across components.
Design Systematic review of randomised controlled trials.
Data sources Cardiovascular randomised controlled trials published in the Lancet, Annals of Internal Medicine, Circulation, European Heart Journal, JAMA, and New England Journal of Medicine, from 1 January 2002 to 30 June 2003. Component end points of composite end points were categorised according to importance to patients as fatal, critical, major, moderate, or minor.
Results Of 114 identified randomised controlled trials that included a composite end point of importance to patients, 68% (n=77) reported complete component data for the primary composite end point; almost all (98%; n=112) primary composite end points included a fatal end point. Of 84 composite end points for which component data were available, 54% (n=45) showed large or moderate gradients in both importance to patients and magnitude of effect across components. When analysed by categories of importance to patients, the most important components were associated with lower event rates in the control group (medians of 3.3-3.7% for fatal, critical, and major outcomes; 12.3% for moderate outcomes; and 8.0% for minor outcomes). Components of greater importance to patients were associated with smaller treatment effects than less important ones (relative risk reduction of 8% for death and 33% for components of minor importance to patients).
Conclusion The use of composite end points in cardiovascular trials is frequently complicated by large gradients in importance to patients and in magnitude of the effect of treatment across component end points. Higher event rates and larger treatment effects associated with less important components may result in misleading impressions of the impact of treatment.
これから)5日ぶりの出勤。定期総会の準備。葬儀後の片付け。線香の咽頭痛で会話不可。

コメント